Omega 3 Deficiency Symptoms: Signs You Might Need More on Keto or Carnivore
Table of Contents
Could You Be Low in Omega 3, Even on a Healthy Diet?
Are you experiencing subtle symptoms like dry skin, fatigue, or difficulty focusing? These could be signs of omega 3 deficiency. Even if you’re following a carnivore or keto diet that prioritizes whole, nutrient-dense animal foods, you might still not be getting optimal levels of these essential fatty acids.
Many low-carb dieters assume that simply eating meat ensures they’re getting all the nutrition they need. While animal-based diets are incredibly nutrient-dense, the specific omega 3 content can vary dramatically based on your food choices within these dietary frameworks.
Omega 3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, are crucial nutrients that support brain function, cardiovascular health, and help regulate inflammation throughout your body. They’re called “essential” for a reason—your body cannot manufacture them, so they must come from your diet.
In this guide, we’ll explore how to recognize the signs of omega 3 deficiency symptoms, explain why this nutritional gap might still exist even on low-carb or carnivore diets, and provide practical solutions to optimize your omega 3 status for better health.
What is Omega 3 & Why It’s Essential
Omega 3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats that play vital roles in your body’s function and overall health. These essential fatty acids cannot be produced by your body and must be obtained through diet or supplementation.
The three main types of omega 3 fatty acids are:
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid) and DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid): These forms, found primarily in animal and marine sources, are the most bioavailable and beneficial forms of omega 3s.
- ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid): Found in plant sources like flax seeds and walnuts, ALA must be converted by your body into EPA and DHA—a process that is often inefficient, with only about 5-15% successfully converted.
Omega 3s are critical for:
- Supporting brain health and cognitive function
- Promoting heart health and healthy blood pressure
- Reducing systemic inflammation
- Supporting cell membrane integrity throughout your body
- Modulating immune system response
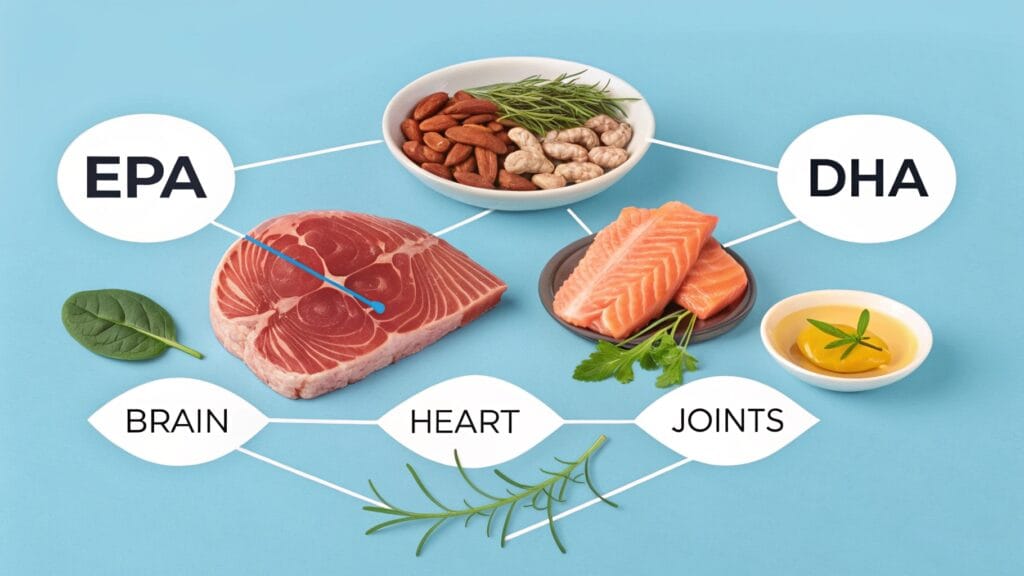
Recognizing the Signs: Common Omega 3 Deficiency Symptoms
Skin and Hair Problems
Dry, flaky skin is one of the most common omega 3 deficiency symptoms. Since omega 3 fatty acids help maintain cell membrane health and regulate oil production in your skin, insufficient levels can manifest as:
- Persistent dry, flaky skin despite adequate hydration
- Increased skin sensitivity or eczema-like rashes
- Slow healing of minor skin injuries
- Dry skin omega 3 deficiency often appears first on exposed areas like hands, elbows, and feet
- Dull or brittle hair and increased hair loss
These skin-related symptoms occur because omega 3s are integral to maintaining your skin’s moisture barrier and regulating oil production. Without adequate omega 3s, your skin cells can’t retain moisture effectively.
Fatigue and Low Energy
If you’re experiencing persistent fatigue despite getting adequate sleep, low omega 3 levels might be contributing to your energy issues. Fatigue lack of omega 3 can manifest as:
- Unexplained tiredness even after a full night’s sleep
- Decreased physical stamina during workouts
- Mental fatigue or feelings of general malaise
- “Hitting a wall” earlier than usual during physical activities
Omega 3s support mitochondrial function—your cellular energy factories—and help optimize oxygen utilization in your body, which is why deficiency can impact your energy levels.
Joint Pain and Stiffness
Joint pain omega 3 deficiency is surprisingly common, especially in those following diets that may not prioritize fatty fish consumption. Signs include:
- Morning stiffness in joints that improves with movement
- Unexplained aches in multiple joints
- Increased recovery time after exercise
- Joint discomfort that seems disproportionate to your activity level
The connection between joint pain and omega 3 levels relates to these fatty acids’ potent anti-inflammatory properties. They help produce specialized compounds called resolvins and protectins that actively work to resolve inflammation in your tissues.

Difficulty Concentrating & Memory Problems
Your brain is approximately 60% fat, with DHA (a form of omega 3) making up a significant portion of its fatty acid composition. Brain fog omega 3 deficiency can present as:
- Trouble maintaining focus during tasks
- Mild, unexplained memory lapses
- Difficulty with word recall or “tip of the tongue” moments
- Mental fatigue when trying to concentrate
- Decreased cognitive performance compared to your baseline
These cognitive symptoms occur because omega 3s, particularly DHA, are critical for maintaining the integrity and fluidity of brain cell membranes, supporting efficient neurotransmission.
Mood Swings and Mental Health Changes
Omega 3 fatty acids play a crucial role in brain chemistry and neurotransmitter function. Low levels may contribute to:
- Increased irritability or shorter temper than usual
- Mild mood fluctuations throughout the day
- Heightened anxiety or stress response
- Lower mood or decreased motivation
- Emotional reactivity that seems out of character
Research suggests that omega 3s help modulate neurotransmitter function and reduce neuroinflammation, both of which are important factors in mood regulation.
Why Low Omega 3 Can Still Happen on a Low-Carb Diet
Many people assume that simply eating a meat-based diet guarantees optimal omega 3 intake. However, the reality is more nuanced—here’s why you might still experience omega 3 deficiency symptoms even on keto or carnivore:
Not All Animal Products Are Equal in Omega 3 Content
The omega 3 content in animal products varies dramatically based on how the animal was raised:
- Conventional vs. Pastured: Conventionally raised animals fed primarily grain-based diets produce meat, eggs, and dairy with significantly lower omega 3 content compared to their pastured counterparts.
- Muscle Meat Focus: If your carnivore or keto diet emphasizes mostly muscle meats (steaks, chicken breast, etc.) without including fatty fish or organ meats, you may be missing concentrated sources of EPA and DHA.
The Critical EPA/DHA Sources
The most beneficial forms of omega 3 (EPA and DHA) are highest in:
- Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and herring
- Seafood, particularly shellfish
- Some organ meats, especially from grass-fed animals
- Pastured egg yolks
If these foods don’t make regular appearances in your low-carb meal plan, you might be experiencing an omega 3 gap.
The Omega 3:6 Ratio Matters
While low-carb and carnivore diets naturally improve the omega 3:6 ratio by eliminating inflammatory seed oils (high in omega 6), the absolute quantity of omega 3 in your diet still matters.
Even with an improved ratio, if your total intake of EPA and DHA remains low, you may still experience omega 3 deficiency symptoms. This is especially true if you have increased needs due to factors like:
- High physical activity levels
- Chronic stress
- Inflammatory conditions
- Genetic factors affecting metabolism of fatty acids
Optimizing Your Omega 3 Intake: Low-Carb Solutions
Prioritize EPA/DHA-Rich Foods within Your Diet
The most straightforward way to increase your omega 3 intake on a carnivore or keto diet is to strategically include foods naturally high in EPA and DHA:
Fatty Fish & Seafood:
- Wild-caught salmon (3-4 oz provides approximately 1,500-2,000mg of omega 3s)
- Sardines (among the highest omega 3 content per serving)
- Mackerel (particularly high in both EPA and DHA)
- Herring and anchovies (excellent sources that are often overlooked)
- Oysters and other shellfish (provide DHA along with other important nutrients)
Try to include fatty fish at least 2-3 times per week for optimal omega 3 levels.
Quality Animal Products:
- Eggs from pastured hens (much higher in omega 3s than conventional eggs)
- Grass-fed and finished beef (contains approximately 2-5 times more omega 3s than grain-fed)
- Grass-fed lamb (naturally higher in omega 3s)
- Organ meats from pastured animals (particularly liver)
Build your diet around nutrient-dense animal foods. See our complete Carnivore Diet Food List for more options.
Balance Omega 3s with Omega 6s
One advantage of carnivore and keto diets is naturally reducing omega 6 intake by eliminating processed foods and seed oils. This improved ratio means you may need less total omega 3 compared to someone eating a standard Western diet high in omega 6s.
Key strategies:
- Avoid industrial seed oils completely
- Choose animal fats from pastured sources when possible
- If including nuts on keto, favor lower omega 6 options like macadamias

When to Consider Omega 3 Supplementation
Even with focused dietary choices, there are situations where supplementation might be necessary to address omega 3 deficiency symptoms:
- You don’t regularly consume fatty fish (2-3 times weekly)
- You have specific health concerns that may benefit from higher doses
- You have limited access to high-quality, pasture-raised animal products
- Blood testing indicates suboptimal omega 3 levels
- You have genetic factors affecting fatty acid metabolism
Types of Supplements
If you decide to supplement, several forms of omega 3 supplements are available:
- The most common and researched form
- Look for triglyceride form rather than ethyl esters for better absorption
- Varies widely in quality and concentration
- Contains omega 3s bound to phospholipids, potentially enhancing absorption
- Naturally contains astaxanthin, an antioxidant that helps prevent oxidation
- Generally lower concentration of EPA/DHA per serving than fish oil
- Contains omega 3s plus vitamins A and D
- Traditional, whole-food supplement option
- Lower concentration of EPA/DHA than concentrated fish oils
Algae Oil (for those including minimal plant foods):
- Plant-based source of DHA and some EPA
- Good option for those avoiding all animal products
Quality is CRITICAL
Not all omega 3 supplements are created equal. Poor quality supplements may be:
- Oxidized (rancid) before you even open the bottle
- Contaminated with heavy metals or other pollutants
- Significantly lower in actual EPA/DHA content than claimed
- Using less bioavailable forms of omega 3
Look for supplements that are:
- Third-party tested (IFOS certification is gold standard)
- Tested for heavy metals, PCBs, and other contaminants
- Clear about the actual EPA/DHA content per serving (not just “total omega 3s”)
- Using triglyceride form rather than ethyl esters when possible
- Properly packaged to prevent oxidation (dark bottles, nitrogen-flushed)
Choosing a pure, potent, and tested Omega 3 supplement is essential. Learn what to look for and see our top recommendations in our detailed guide: [Best Omega 3 Supplements for Low-Carb & Carnivore Dieters] (coming soon).
Getting Tested for Omega 3 Levels
If you’re experiencing persistent omega 3 deficiency symptoms or want to optimize your levels with precision, consider testing your omega 3 status.
The most reliable test is the Omega-3 Index, which measures the percentage of EPA and DHA in red blood cell membranes. This provides a more accurate picture of your long-term omega 3 status compared to standard blood tests.
Interpreting Results:
- Below 4%: Deficient (high risk)
- 4-8%: Intermediate
- Above 8%: Optimal range
Consider discussing this test with your healthcare provider, especially if you’ve been experiencing multiple potential omega 3 deficiency symptoms.
For a broader look at important metabolic markers, including Omega 3 levels, see our guide to [Testing Your Metabolic Health] (coming soon).
Important Considerations & Medical Disclaimer
Potential Side Effects
While increasing omega 3 intake through food is generally safe, supplements can sometimes cause:
- Fishy aftertaste or breath (reduced with high-quality products)
- Minor digestive discomfort, especially at higher doses
- Extended bleeding time in some individuals
Potential Interactions
Omega 3 supplements may interact with:
- Blood-thinning medications (including aspirin)
- Blood pressure medications
- Medications affecting blood sugar
Special Warnings
Exercise caution with:
- Very high doses (above 3g EPA+DHA daily) without medical supervision
- Upcoming surgeries (omega 3s may increase bleeding time)
- Seafood allergies (some fish oil supplements may trigger reactions)
MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: This article is for educational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes or starting any supplement regimen, especially if you have existing medical conditions, take medications, or are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Conclusion: Optimize Your Omega 3 Status for Better Health
Recognizing omega 3 deficiency symptoms is an important step toward optimizing your health on a low-carb or carnivore diet. Despite the many benefits of these dietary approaches, strategic attention to omega 3 intake remains necessary for most people.
By prioritizing fatty fish and high-quality animal sources in your diet, you can significantly improve your omega 3 status naturally. For those who need additional support, carefully selected supplements can be a valuable tool when chosen with quality and purity in mind.
Optimizing your omega 3 levels supports overall metabolic health, enhances brain function, promotes cardiovascular health, and helps manage inflammation—complementing the already powerful benefits of your low-carb or carnivore lifestyle.
Have you experienced omega 3 deficiency symptoms? How did you address them on your low-carb diet? Share your experience in the comments below!
Related Articles:
- What is Insulin Resistance Explained
- Can You Reverse Type 2 Diabetes
- Carnivore Diet Food List
- Carnivore Diet Supplements: Electrolytes
- What Are Adaptogens
- 10 Keto Carnivore Brain Foods for 2025
- Carnivore Diet Supplements
- Carnivore Diet Recipes
MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: This article is for educational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes or starting any supplement regimen, especially if you have existing medical conditions, take medications, or are pregnant or breastfeeding.
AFFILIATE DISCLAIMER: This post contains affiliate links. If you click on these links and make a purchase, I may receive a small commission at no extra cost to you. These commissions help support this blog and allow me to continue providing free content. I only recommend products I personally use and trust.
Enjoy, Review – We Value Your Opinion!
There are no reviews yet. Be the first one to write one.

